INTUSK MAGAZINE
TO THE CORE OF YOUR HEART
Planets In The Solar System - Venus
February 8, 2023
Venus is the second closest planet to the Sun. It takes the Earth 224.7 days to orbit the Sun. This is the brightest natural object in the sky other than the moon. Since Venus is an insignificant planet, it does not appear to travel very far from the Sun when viewed from Earth. Its maximum length is 47.8. The maximum brightness of Venus is seen before sunrise and after sunset. As a result, it is also known as the Morning or Evening Star.
The terrestrial planet Venus is considered to be Earth's sister because of their similarity in size, gravity, and composition. This was a matter of great curiosity until twentieth-century astronomy revealed some secrets. Venus has the densest atmosphere among the terrestrial planets. It is high in carbon dioxide. This is because there are no organic organisms in it to give carbon back to rocks and other surface objects or to absorb carbon into the biomass. has become a desert. The best explanation for this is that Venus did not have a magnetic field, so the water that evaporated from the oceans may have decomposed and the released hydrogen gas may have been drawn into interplanetary space. The atmospheric pressure on the surface of Venus is 92 times that of Earth.
Observation
The brightness of Venus, which is even brighter than the brightest stars, ranges from 3.8 to 4.6. This makes it bright enough to see even at noon and can be easily seen as the sun goes down. As an asteroid, it is always within 47 degrees of the Sun.
In its orbit around the sun, Venus orbits the Earth every 584 days. The star can be seen before sunset and is then visible just before sunrise. The other asteroid, Mercury, reaches its maximum elongation of 28 degrees, but it is difficult to see at sunset, whereas Venus is not easily missed. Because of its brilliance, it can be seen in the dark sky long after sunset. Flying saucers are often misreported as Venus.
As it orbits, the phases of Venus are indicated by the phases of the moon. As it moves between the Earth and the Sun, it is like a new moon; when it is on the opposite side of the Sun, it is completely from the Sun, and when it has the maximum elongation from the Sun, it is like a half-moon. Venus is brightest when it takes the shape of a thin crescent. This is when it is closest to the earth.
The orbit of the Venus trainee is slightly below the orbit of the Earth. It does not follow the face of the sun as it moves between the various suns and the earth. Ashen light has long been a question in the calculation of Venus. or the dim light that appears on the player's dark side. This was first done in 1643. There are two theories as to whether this light is caused by the electrical activity of Venus' atmosphere, and whether it is a visual illusion caused by the physical effects of looking at a very bright crescent-shaped object. Galileo (Galileo Galilei) proved that Venus orbits the sun.
Venus was known as Shulkra in Hindu astrology and the Wondering Star in the West. In the past, Venus was considered two stars, the "Morning Star" and the "Evening Star".But they did not know that they could see the same planet differently. Pythagoras was the first to recognise that this was a single object.
By observing the movements of Venus in the 17th century, Galileo discovered that it did not orbit the earth like the moon. At the same time, the concept of planetary orbits around the sun was introduced. Johann Schroter observed in 1970 that Venus had an atmosphere. Observations of Venus 'dark region also confirmed that Venus' sun has a temperature of 1800 °C in the open. Due to this atmosphere, it was difficult to determine the rotation time. Giovanni Cossin and Johann Schroter concluded that there was a 24-hour rotation period, but this was not correct.
Land-based tests With the advancement of UV, radar, and telescopes, more accurate data about Venus became available in the 20th century. During UV observations, data not detected by JR rays were found. Frank. According to E. Rose, the cause is Venus' cloud. 90% of Venus has a solid surface. Attempts to detect the rotation time of Venus using Doppler light reflections have failed. Vestor Slipher performed this experiment and concluded that the reason for the failure was that Venus' rotation time was large. In 1950, the rotation of Venus was discovered to be retrograde. The use of radar recorded a period of rotation close to the new values.
1970s Radar experiments revealed a wealth of information from the Arecibo Observetory to Venus' highly reflective regions and rays. Here, information about the nature of the land is important Here information about the nature of the land is important. Here we came across a mountain range called the Moxwell montes. The best radar photo was taken from Earth. M. Spreads in a range of about 50 km.
External Nature
Venus is a terrestrial planet. There are four such planets in the Solar System, including Earth. All other planets are gases. Venus is very similar to Earth. Its diameter is about 1 km larger than the Earth. M. 650 less than 81.5% of the Earth's mass. But the internal conditions of Venus are different from those of Earth. Its atmosphere contains 96.5% carbon dioxide and 3.5% nitrogen.
From the external similarities between Earth and Venus, it can be concluded that the interior is very similar to the Earth's interior. Therefore, it can be assumed that the core of Venus is liquid. Venus does not have earthquakes like Earth. Its terrain is dry and low, and this cold environment expels the magnetic field of the poles.
The Nature of Orbital Motion
The orbital speed of Venus is about 9.69 km / s. It takes about 29 years for the planet to complete one complete orbit around the Sun. The elliptical orbit of the planet is 2.480 degrees relative to the orbital plane of the Earth.
The rotational speeds of the visible features on Venus affect latitudes, and multiple multiplier rotation periods have been found for different regions. The duration of the "System" labelled zone is 10 hours 14 minutes and 00 seconds, while the duration of the "System" is 10 hours 39 minutes and 24 seconds. The rotation time of the "system" is 10 hours 39 minutes 22.4 seconds
No period of rotation has been found inside the planet. In 2004, the Cassini spacecraft revealed that the period of radio rotation of Venus had increased significantly.
It has been revealed that the rotation of radio emissions depends on another factor besides the rotation of the planet. That is the factor of convection plasma disc. This depends on other factors besides the orbit of the planet. It has been theorized that the water vapour emitted by Venus 'satellite "Encelasis" affects Venus' magnetic field and that radio emissions may be one reason for the separation of measurements over time.
According to data released in 2007 by Cassini, Voyager and Paganier, the orbit of Venus in September 2007 was recorded as 10 hours 32 minutes 35 seconds.
Orbit and Rotation
The distance from Venus to the Sun is about 108 million kilometres, and it completes its orbit every 224.65 days. Although all planetary orbits are elliptical, Venus' orbit is approximately circular. Its eccentricity is less than 0.01. The position of Venus between the Sun and the Earth, known as the "inferior conjunction," is the closest planet to Earth. Then the distance between Earth and Venus is about 40 million kilometres. Every 584 days, Venus meets this lower body. Venus rotates every 243 days, the lowest speed on any major planet.
However, Venus' solar day is shorter, with 116.5 days from one sunrise to the next. The sun rises in the west and sets in the east. The surface of Venus rotates at its equator at a speed of 6.5 km / h, and at the equator, the Earth's rotation speed is about 1 km / h. 1600. Most planets orbit in the opposite direction (counterclockwise) to the Sun when viewed from the North Pole.
But Venus orbits in a clockwise direction. Scientists were intrigued by the low rotation speed of Venus and its orbiting in the opposite direction. Scientists have calculated that during the early days of Venus' existence, it may have had higher rotational speeds and orbits in the direction of other planets, but may have had such a low rotational speed due to the effect of tidal waves on its dense atmosphere for billions of years.
Venus does not yet have a moon, but the asteroid 2002 VE 68 has a semi-orbital relationship to it. Some believe that one of the moons may have had Venus in of years ago, and that another collision may have changed the direction of the planet's rotation. They also point out that due to the change in the direction of rotation, Venus' moon may have been spiralling towards Venus and coinciding with it.
Structure
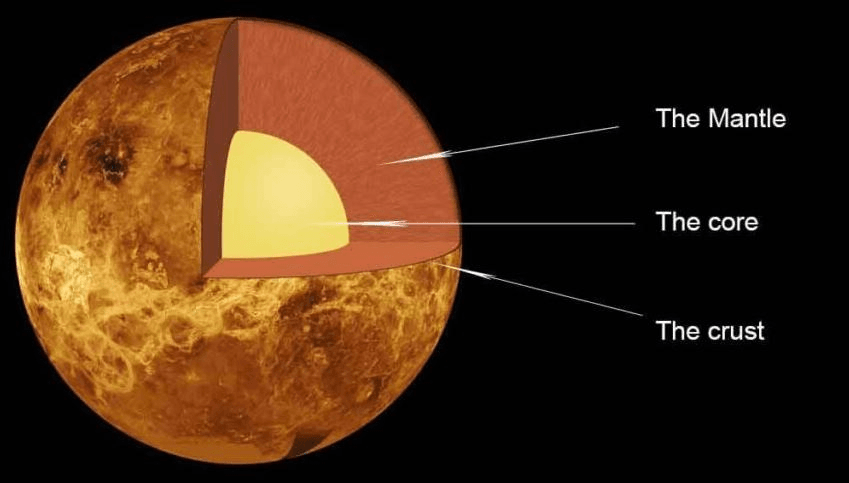
Although little is known about the internal structure, the fact that the Earth and Venus are similar in size suggests that it has a similar internal structure. It consists of a nucleus and a crust, and the core of Venus, like Earth, is at least partially or slightly liquid. The small size of Venus suggests that the deep interior pressures are significantly lower than Earth's. The main difference between the two planets is that Venus has no topography. The reason seems to be the dry surface and permeability. As a result, the planet's heat dissipation is minimised, thus preventing it from cooling, which also contributes to the absence of an internally generated magnetic field.
Core and Magnetic Field
In 1980, the Pioneer Venus orbit discovered that Venus' magnetic field was smaller and weaker than Earth's. The formation of such a small magnetic field (close to the planet) is triggered by an interaction between the ionosphere and the solar wind. But the Earth's magnetic field is induced by the inner dynamics of the core. Venus' magnetic field is insufficient to protect the atmosphere from cosmic radiation.
This inherent magnetic field of Venus is amazing because it is a smaller planet than Earth. It is further stated that it also contains a generator at its core. A generator needs three things. That is a conductive fluid, a rotation, and convection. The core is assumed to be electrically conductive. However, its rotation is assumed to be very slow. But simulations show that it is adapting to generate a generator.
This suggests that the lack of a generator is due to a lack of convection in the core of Venus. On Earth, convection occurs in the outer two layers of the core. This is because the bottom of the two layers is hotter than the surface. Venus does not have the terrestrial anomalies that can release heat, so it may not have a solid inner core. Or the core may not be as cool as it used to be, so the entire core of the core is at approximately the same temperature. Another reason is that its essence is not yet complete.
Atmosphere
Venus' atmosphere is very dense. It is mainly composed of small amounts of carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Atmospheric mass is 93 times the atmospheric mass of the Earth. The surface pressure is 92 times that of the Earth's surface. It is equivalent to the pressure of an ocean depth of 1km on Earth. At a surface density of 65 kg / m3 (6.5% of which is water), the strongest greenhouse effect in the Solar System is generated by the SO2 dense clouds and the CO2-rich Venusian atmosphere. The surface temperature is 4600C. Thus, the surface temperature of Venus is higher than the surface temperature of Mercury with a minimum temperature of -2200C and a maximum temperature of 4200C.
However, Venus is twice as far away from the Sun as Mercury and receives about 25% of Mercury's solar refraction. As Venus has no moisture, the relative humidity of its surface is negligible. Therefore, the temperature index ranges from 4500°C to 4800°C. Studies show that the atmosphere of Venus billions of years ago was more similar to the Earth's atmosphere today. And that there was sometimes a considerable amount of liquid water on the surface. The presence of heat transfer in the atmosphere below Venus by thermal conditions and winds suggests that Venus' surface does not fluctuate significantly during the day and night. Due to the slow rotation of the planet, the surface winds being a few kilometres per hour, and the high density of the surface atmosphere, they exert considerable force against resistance.
It also transports dust and small pieces of rock. Temperature is not an issue, but it is questionable whether a person can walk on its surface. Above the solid CO2 layer, solid clouds of SO2 and H2SO4 can be seen. They reflect 60% of the sun's light and prevent direct exposure to visible light on Venus' surface. Although Venus is closer to the Sun than Earth, it does not receive much sunlight due to this permanent cloud cover. In the absence of the greenhouse effects of CO2 in the atmosphere, Venus' surface temperature is very similar to that of Earth. Extreme winds of up to 300 km / h occur every 4 to 5 days on Earth.
2007 Venus Express observes large, dual atmospheric hurricanes at the planet's south and south poles.
Surface
The Vero 7 spacecraft was built to withstand high pressure so that it could go to the surface of the planet Venus and return with data. It was frozen before entering Venus, and a special parachute was mounted to allow the spacecraft to land within 35 minutes. Entering the atmosphere on December 15, 1970, the Venus spacecraft's torso was torn as it landed, but it was not serious but crashed into the surface of the alien planet. The spacecraft skidded to the ground and landed on Venus on December 5, 1970, by parachute. But this landing was not very successful.
The plane did not crash, but it is believed to have crashed. The plane crashed after giving a weak signal of surface temperature for 23 minutes. The Venera 8 spacecraft transmitted data over Venus for 50 minutes. Venera 9 and Venera 10 were then shipped. Venera 10 transmitted the photo for the first time. Venera 9 fell on a steep slope, and Venere 10 fell on a rock like a "baselt". The Marinor 10 spacecraft sent to the United States to test gravitational fields passed Mercury past Venus on February 5, 1974. Where it is about 1 km from Venus. At a distance of 5790 km, the spacecraft transmitted more than 4,000 photographs. When UV was used, even clouds that could not be observed from Earth were found.
There were 82 operations under the Pioneer Venus project in the United States. Pioneer Venus Orbiter's first mission was to orbit Venus. Launched on December 4, 1978, the spacecraft remained on the surface of Venus for more than 13 years and was examined by radar. Five observation spacecraft under the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe performed on December 5, 1978, observing Venus' common and hot air currents. The following year, four aircraft landed as Venera 11-14. Venera 11 and 12 observed thunderstorms. Venera 13 and 14 landed on March 1 and 5, 1982, respectively. These aircraft transmitted the first colour photograph. Each of these spacecraft is about 50 km from the surface of Venus. Due to the density of the lower atmosphere, the landing was accurate.
Venera 13 and 14 were tested using an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. Venus 15 and 16 observed the surface of Venus using a "synthetic aperture radar". The Venera project ended with those two planes. Russia launched a project in 1985 to observe the comet Venus and Haley. Prior to the comet's observation, two spacecraft from the Vega Project sent spacecraft to Venus. This action was not successful on the Vega 1 aircraft. These balloon-propelled observation planes took off.
The pressure at this point was equal to the pressure of the earth. 46 hours of transmitted data revealed that there were strong winds and strong convection cells on the surface of Venus.
Past Studies
Galileo (Galileo Galilei) proved that Venus orbits the Sun. In Hindu astrology, Venus was known as Shulkra and in the West as Wondering Star. In the past, Venus was considered to have two stars, the Morning Star and the Evening Star. But they did not know that they see the same planet differently. Pythagoras was the first to recognise that this was a single object. By observing the movements of Venus in the 17th century, Galileo discovered that it did not orbit the earth like the moon. At the same time, the concept of planetary orbits around the sun was introduced. Johann Schroter observed in 1970 that Venus had an atmosphere. Observations of Venus' dark region also confirmed that the Sun has a temperature of 1800 °C in the open. Due to this atmosphere, it was difficult to determine the time of rotation. Glovenni Cossin and Johann Schroter concluded that there was a 24-hour rotation period, but this was not correct.
Land-Based Tests
With the advancement of UV, radar, and telescopes, more accurate data on Venus was obtained in the 20th century. During UV observations, data not detected by JR rays were found. According to Frank. E. Rose, the cause is Venus' cloud. 90% of Venus has a solid surface. Attempts to detect the rotation time of Venus using Doppler light reflections failed. Vestor Slipher performed this experiment and concluded that the reason for the failure was that Venus' rotation time was large.
In 1950, the rotation of Venus was discovered to be retrograde. The use of radar recorded a period of rotation close to the new values. 1970s radar experiments revealed a large amount of information from the Arecibo Observetory by emitting rays to and from Venus' highly reflective regions. Here, information about the nature of the land is important. Here we came across a mountain range called the Moxwell montes. The best radar photo taken from Earth. M. Spreads in a range of about 50. Venera - 3 landed on Venus on March 1, 1966. It was the first man-made spacecraft to enter the atmosphere of a planet and collide with it.
However, the telecommunications system was down before it could provide any information about the planet. On October 18, 1967, Venera-4 successfully entered the atmosphere and underwent a number of scientific experiments. Then the unmanned spacecraft entered Venus for the second time. Venera - 4 revealed that the surface temperature was higher than the 50000C calculated by Mariner - 2, and that carbon dioxide made up 90% to 95% of the atmosphere. Because the density of Venus' atmosphere was higher than that predicted by the Venera - 4 makers, the parachute's descent was slower than expected, and the cells disintegrated before reaching the surface.
After 93 minutes of descending data, the Venera-4 final pressure reading was 18 bar at an altitude of 24.96 km. On October 19, 1968, another spacecraft entered Venus, flying 4000 km above the clouds of Mariner-5. Mariner-5 was specifically designed to replicate Mars-related Mariner-4. But when the mission was successful, the spacecraft was reassembled for Venus operations. A set of instruments more sensitive than the Mariner-2 was used, and radio input tests provided data on the pressure, density, and constituents of Venus' atmosphere. The Venera - 4 and Mariner - 5 data analysis was analyzed by a separate Soviet-American consortium and provided examples of space cooperation the following year.
Armed with lessons and data from Venera-4, the Soviet Union launched the Venera-5 and Venera-6 twin spacecraft into a five-day mission in January 1969. They reached Venus on May 16 and May 17 of that year. Their crust was designed to withstand a pressure of 25 bar. It was also fitted with a small parachute for a rapid descent. Since then, Venus' atmospheric models have expected a surface pressure of between 75 and 100 atmospheres and were never expected to remain at the surface. After more than 50 minutes of atmospheric data, both planes crashed before reaching the surface of Venus' night sky at an altitude of about 20 miles [20 km].



